Interesting examples of IoT in healthcare
The first and most important goal of the IoT is to improve the quality and also simplify the life of the people. In fact, IoT is going to eliminate the issues that engage your mind to let you focus on more important matters. Help to healthcare is also one of the factors contributing to the […]
The first and most important goal of the IoT is to improve the quality and also simplify the life of the people. In fact, IoT is going to eliminate the issues that engage your mind to let you focus on more important matters. Help to healthcare is also one of the factors contributing to the improvement of the quality of life. We will refer to some examples of IoT applications in the field of healthcare and treatment in this article.
The first and most important goal of the IoT is to improve the quality and also simplify the life of the people. In fact, IoT is going to eliminate the issues that engage your mind to let you focus on more important matters. Help to healthcare is also one of the factors contributing to the improvement of the quality of life. We will refer to some examples of IoT applications in the field of healthcare and treatment in this article.We are witnessing the fusion of technology with our lives. In fact, you can’t look at the corner of your home or business and don’t see the technology footprint there. Even if you have not used specific technology anywhere in your home or office, certainly you can list options in your mind. Meanwhile, the gap between developing and introducing a technology and its entry into our everyday lives has become much shorter. While some technologies passed the path of commercialization for more than a decade, today we are faced with cases that this path is less than a year.
Since the field of health and treatment has always been at the forefront of human life, the use of the latest technologies to achieve the best possible results, as well as the highest level of controllability, has become a principle. Using various types of lasers, advanced imaging equipment, and other examples prove that this field is always ready to accept the new capabilities of the technology. In the same vein, due to the expansion of the use of the Internet and connected devices, the IoT has become an opportunity to take advantage of these possibilities, and it is natural that the health and treatment also do not lose such an occasion. The two parameters of communication and ubiquitousness of the Internet make it possible for physicians to take certain measures to treat patients or to know about their condition remotely, even without the intervention of themselves. In the following, we will refer to several IoT applications in health-related sectors.
Activity tracking during cancer treatment
The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), a Cancer Research and Treatment Institute, in collaboration with Medidata, a Cloud research firm, is investigating the use of activity trackers to collect information about patients treated with multiple myeloma treatment.
Patients should wear these detectors from a week before starting treatment until the end of their several months of treatment. In this way, the state of activity and fatigue of the patient, as well as his state of hunger and appetite are recorded. All of this data is stored in the Medidata Patient Cloud ePRO application.
In this way, researchers and physicians can accurately follow the process of effective therapeutic interventions on the patient’s condition and compare the outcomes.
Connected inhalers
One of the most important matters in the treatment process is the patient’s c to the doctor’s treatment plan. So, various teams are trying to get a detailed report of the patient’s compliance status with the doctor’s instructions by embedding sensors in medications or delivery systems.
Novartis that is a pharmaceutical company has launched extensive research efforts with two Propeller Health and Qualcomm companies to develop a type of inhaler capable of communicating with smart devices for patients suffering from COPD. COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is a type of pulmonary obstruction that dramatically influences the lives of affected patients.

With the development of its new product, Novartis plans not only to provide reminders for patients but also to record their compliance with the treatment process, so that it can check the effectiveness of the drugs and the entire treatment process.
Ingestible sensors
Another example of the process of tracking the patient’s adherence to the doctor’s treatment plan. Here, Proteus Digital Health employs sensors in antipsychotic as well as hypertension pills. After the patient takes his medication, the pill dissolves in his stomach and produces a small signal. This signal is received by the receiver on the patient’s body and then relayed to an app on his smartphone.

Connected contact lenses
Alcon, a subsidiary of Novartis, has licensed Google’s smart lens technology. This technology deals with non-invasive sensors that are embedded in the lens.
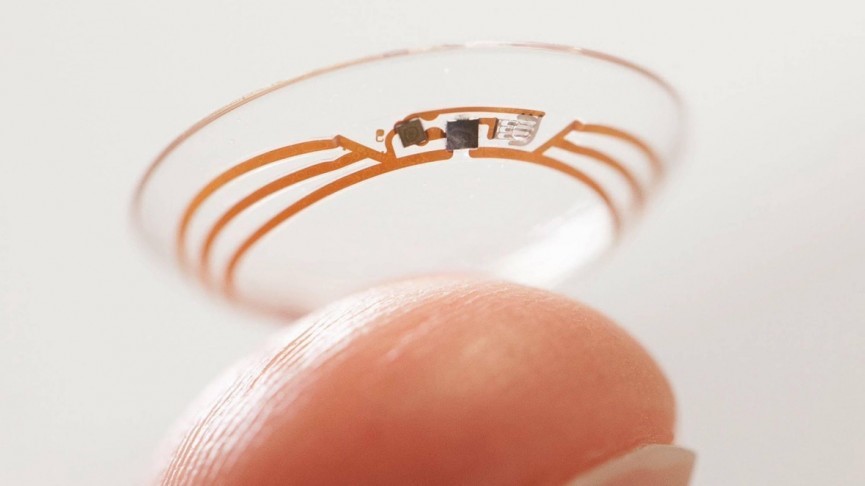
Contact lenses may eventually measure the glucose levels of people with diabetes by analyzing their tears, and then send this information to an app on their smartphone. Novartis also hopes to make smart lenses for those with presbyopia. If the company reaches its goal in this area, those who suffer from presbyopia can regain their eye’s focus.
OpenAPS
Mrs. Dana Lewis, who has diabetes and should regularly test her blood glucose and use insulin, along with her husband, Scott Leibrand, have made an exciting experience. More precisely, the couple hacked a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system and an insulin pump with the help of a Raspberry Pi computer.
The Open Artificial Pancreas System (OpenAPS) is a combination of those three components. The data collected by the CGM and the Raspberry Pi computer, allow a software developed by themselves to control the amount of insulin injected by the pump, continuously.
The couple has released their open source software, and several patients have used it to hack their own equipment. Perhaps this is one of the cases that patients are thinking of taking advantage of existing features and technologies sooner than companies and research centers.